AI Ethics: Key Ethical Challenges & Solutions (2025)
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming our world, influencing everything from how we communicate to how we diagnose diseases. While AI offers tremendous potential for innovation, it also raises important ethical questions.
This article examines the ethical issues related to AI and the challenges of incorporating AI technologies into society.
Key Takeaways:
- Bias and Fairness: Actively work to identify and mitigate biases in AI systems.
- Transparency and Accountability: Develop explainable AI models and take responsibility for their outcomes.
- Ethical Guidelines: Follow established principles and support government regulations that promote responsible AI.
- Human-centric Approach: Ensure AI technologies enhance human well-being and respect human rights.
Understanding Artificial Intelligence
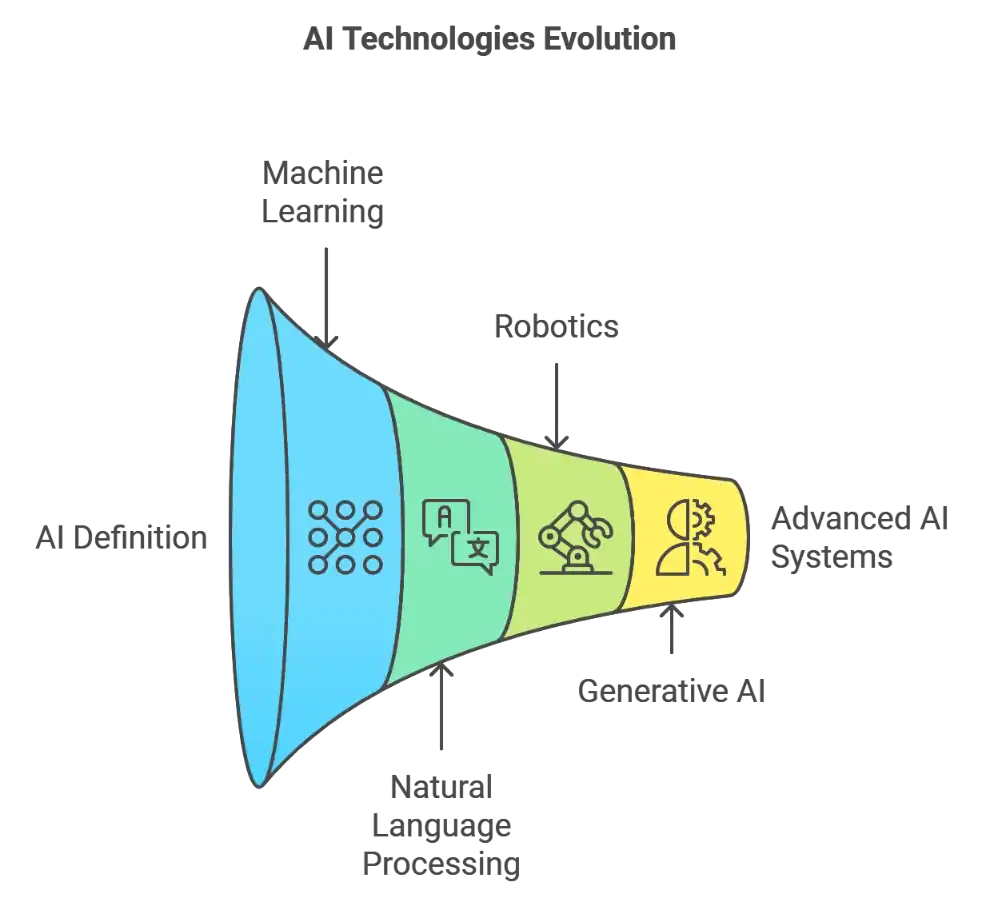
AI technologies include machine learning, natural language processing, robotics, and more recently, generative AI systems capable of creating content like text, images, or music.
AI Capabilities and Applications
- AI algorithms: used for data analysis and decision-making in various industries.
- AI Models: implemented in applications such as virtual assistants, recommendation systems, and autonomous vehicles.
- AI Tools: Software and platforms that enable AI functionalities, like image recognition or language translation.
The Ethical Implications of AI
Every day, AI systems make millions of decisions. They decide who gets a loan. Who sees a job posting. Who gets flagged at airport security. These aren’t future problems—they’re happening now.
The thing is, most people don’t even know when AI is making decisions about their lives. That mortgage application you submitted? An algorithm probably rejected it before a human ever saw it. That perfect job you never heard back from? AI might have tossed your resume in the digital trash.
The Bias Problem Nobody Wants to Fix
Here’s what happens when you train AI on human data: it learns human prejudices. Amazon discovered this the hard way when their AI-powered hiring tool started discriminating against women. The system learned from 10 years of resumes—mostly from men—and decided that being male was a qualification.
Common AI Biases:
- Racial bias in facial recognition (error rates up to 35% higher for darker-skinned individuals)
- Gender bias in language processing
- Economic bias in credit scoring algorithms
- Geographic bias in delivery and service algorithms
The companies building these systems know about these problems. They just don’t always care enough to fix them before launching.
Who’s Responsible When AI Screws Up?
Picture this: A self-driving car hits someone. Who goes to jail? The programmer who wrote the code? The company that made the car? The person sitting in the driver’s seat playing Candy Crush?
This isn’t some philosophical thought experiment. It’s a real question courts are trying to answer right now. And nobody has good answers yet.
The Accountability Gap
When humans make mistakes, we know who to blame. When AI makes mistakes, everyone points fingers:
| Who Gets Blamed | What They Say |
|---|---|
| Developers | “We just built what we were told” |
| Companies | “The algorithm made the decision” |
| Users | “We trusted the technology” |
| Regulators | “We’re still figuring out the rules” |
Meanwhile, real people suffer real consequences from AI decisions they can’t appeal or even understand.
Principles of Ethical AI
To address these challenges, several ethical principles guide AI development, including:
-
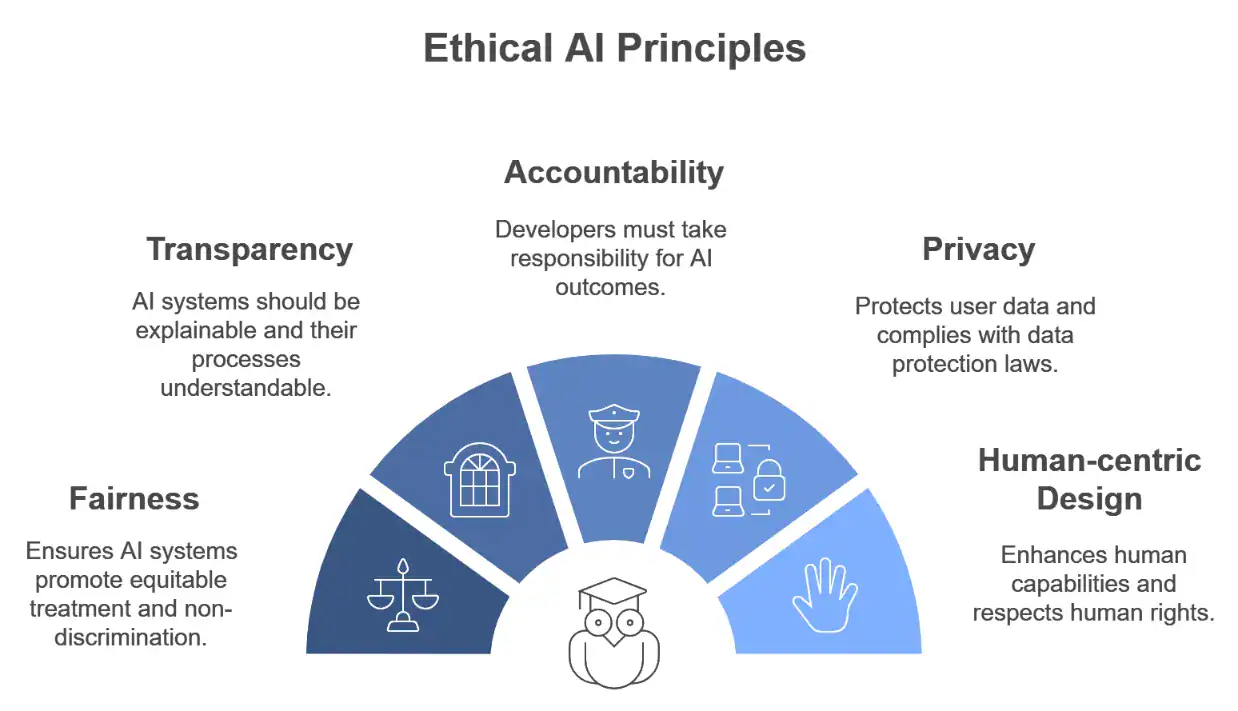
- Fairness: AI should not discriminate and should promote equitable treatment.
- Transparency: AI systems should be explainable and their decision-making processes understandable.
- Accountability: Developers and organizations must take responsibility for AI outcomes.
- Privacy: AI must protect user data and comply with data protection laws.
- Human-centric design: AI should enhance human capabilities and respect human rights.
The Privacy Trade-Off Everyone Ignores
AI needs data like cars need gas. The more data it has, the better it works. But that data comes from somewhere—it comes from us.
Every time you:
- Post on social media
- Use a fitness tracker
- Shop online
- Drive with GPS on
- Talk to a smart speaker
You’re feeding the machine. And once that data is out there, good luck getting it back.
What AI Knows About You
Modern AI systems can predict:
- When you’re likely to get sick
- If your relationship is failing
- Your political beliefs
- Your sexual orientation
- Whether you’re pregnant (sometimes before you know)
Companies say they anonymize this data. But researchers keep proving that anonymous data isn’t really anonymous. With enough data points, AI can figure out exactly who you are.
The Job Apocalypse That’s Already Started
Everyone talks about robots taking jobs in the future. But AI is already replacing workers today—just quietly.
Jobs AI Is Already Doing:
- Writing basic news articles
- Reviewing legal documents
- Diagnosing diseases
- Trading stocks
- Screening job applications
- Creating marketing content
- Answering customer service calls
The people who lost these jobs didn’t see it coming. One day they had work, the next day an algorithm did it cheaper and faster.
The Skills Gap Nobody’s Bridging
Here’s the cruel irony: The same companies replacing workers with AI say they can’t find qualified people to build and manage these systems. They’re creating a world where you either work on AI or get replaced by it.
Meanwhile, retraining programs are a joke. You can’t turn a 50-year-old truck driver into a machine learning engineer with a six-week coding bootcamp.
Real-Life Applications and Ethical Challenges
Practical Applications
This HTML Tool about AI Content Grader converts theoretical ethics discussion into actionable tool:
AI Content Grader
Analyze your content's originality, SEO potential, and readability
Originality
SEO Potential
Readability
Recommendations
Healthcare
AI technologies are revolutionizing healthcare delivery, from diagnosis to treatment planning. However, this integration raises critical ethical considerations about patient privacy and equitable access.
Ethical Challenges:
-
-
- Data Privacy: Handling patients’ sensitive health information requires strict compliance with privacy laws like HIPAA.
- Bias in Diagnosis: AI models trained on limited datasets may not perform well across diverse populations.
-
Real-Life Example:
-
-
- IBM Watson for Oncology was marketed as a tool for cancer treatment recommendations but received criticism for giving unsafe or incorrect advice, as it was trained on synthetic data instead of real patient cases.
-
Financial Services
The financial sector has embraced AI for various applications, including automated decision-making systems that handle everything from credit scoring to fraud detection.
Ethical Challenges:
-
-
- Algorithmic Bias: AI systems might inadvertently discriminate against certain groups in lending decisions.
- Lack of transparency: Customers may not understand how their data affects financial assessments.
-
Real-Life Example:
-
-
- Apple Card Controversy: In 2019, Apple’s credit card was criticized after allegations that its AI algorithm offered lower credit limits to women compared to men with similar financial profiles.
-
Generative AI Tools
Generative AI, like OpenAI’s GPT-3, can create content but raises unique ethical issues.
Ethical Challenges:
-
-
- Misinformation: Potential to generate realistic but false information.
- Intellectual Property: AI-generated content may infringe on existing works.
-
Real-Life Example:
-
-
- Deepfakes: AI-generated videos that realistically swap faces, which can be used maliciously to spread disinformation or harass individuals.
-
Addressing Bias and Ensuring Fairness
Implementing effective strategies to combat AI bias requires a multi-faceted approach.
Strategies:
-
-
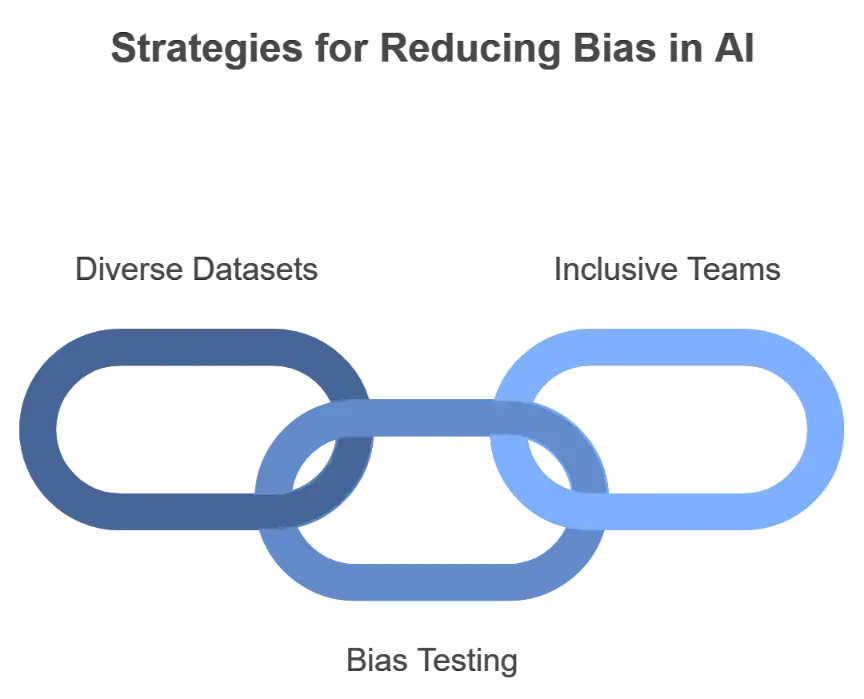
- Diverse Datasets: Use representative data that includes various demographics.
- Bias Testing: Regularly test AI models for biased outcomes.
- Inclusive Teams: Promoting diversity and inclusivity in AI development teams helps bring different perspectives.
-
Table: Techniques for Reducing Bias in AI
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Augmentation | Enriching datasets with diverse examples |
| Algorithmic Fairness Metrics | Using metrics to measure and correct biases |
| Human Oversight | Incorporating human judgment in AI decision-making |
| Transparency Tools | Tools that explain AI decisions to users |
Government Regulations and Ethical Guidelines
Government policies and international frameworks play a vital role in setting ethical standards for AI.
AI Policies and International Frameworks
-
-
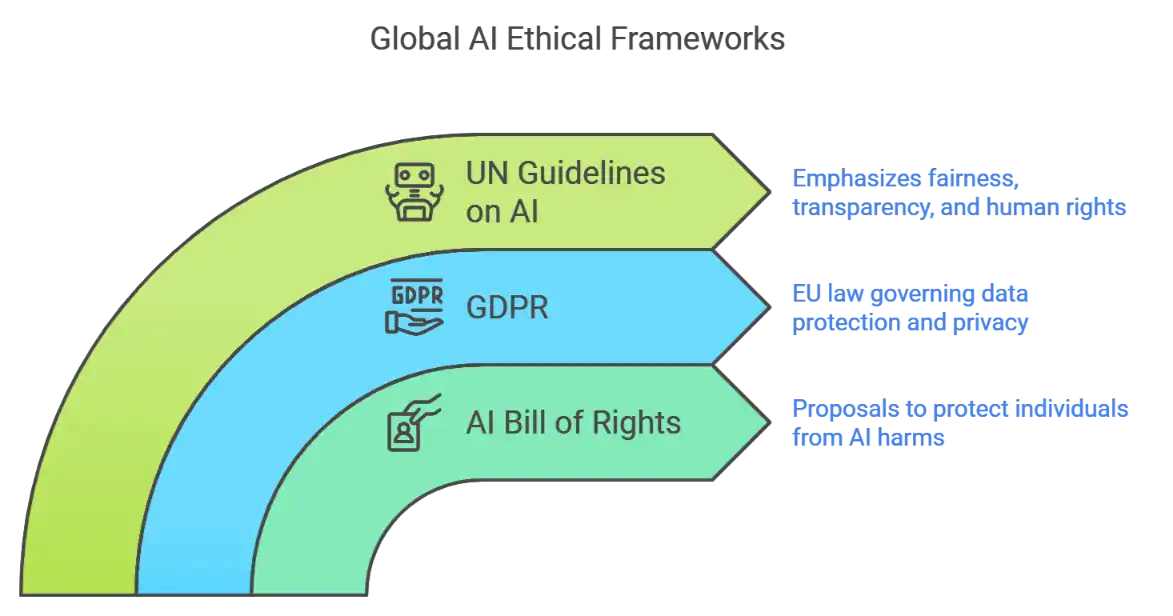
- AI Bill of Rights: Proposals to protect individuals from harms related to AI.
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): EU law that governs data protection and privacy.
- United Nations Guidelines on AI: Emphasize fairness, transparency, and human rights.
-
Real-Life Example:
-
-
- EU’s AI Act: A proposed regulatory framework that categorizes AI applications based on risk and sets compliance requirements to ensure safety and respect for fundamental rights.
-
The Future of AI and Ethics
Artificial General Intelligence
As we look ahead, the evolution of AI technology presents both opportunities and challenges. Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) raises new ethical questions about control and consciousness.
Ethical Considerations:
-
-
- Existential Risks: AGI could potentially surpass human control.
- Moral Status: Debates about whether AGI entities should have rights.
-
AI Adoption and Human Rights
Ensuring that AI adoption respects and promotes human rights is critical.
Ethical Concerns:
-
-
- Surveillance: AI technologies can be used to infringe on privacy.
- Autonomous Weapons: Ethical debates surround AI use in military applications.
-
Real-Life Example:
-
-
- Social Credit Systems: In some countries, AI is used to monitor and rate citizens’ behavior, raising significant privacy and freedom concerns.
-
What Can Actually Be Done?
Talking about problems is easy. Solving them is hard. But here’s what needs to happen:
1. Real Regulation (Not Just Talk)
Governments need to:
- Set clear rules for AI use
- Create penalties that actually hurt
- Require transparency in AI decisions
- Give people the right to appeal AI decisions
- Protect workers from AI replacement
The EU is trying with their AI Act. The US is still figuring out what AI even is.
2. Corporate Responsibility (Stop Laughing)
Companies using AI should:
- Test for bias before launching
- Explain how their AI makes decisions
- Let humans override AI choices
- Pay for retraining displaced workers
- Put ethics before profits
Yeah, I know. But we can dream.
3. Individual Awareness
You need to:
- Know when AI is making decisions about you
- Understand your rights (what few exist)
- Limit the data you share
- Support companies doing AI ethically
- Vote for politicians who get it
Because waiting for corporations to grow a conscience isn’t a strategy.
The Choice We Face
We’re at a crossroads. AI can either be a tool that helps humanity or a weapon that divides us further. The technology itself doesn’t care—it’s just math and electricity.
But the people building it, funding it, and deploying it? They make choices every day. And right now, they’re mostly choosing profits over people.
The ethical implications of AI aren’t some far-off concern. They’re here, now, affecting real people in real ways. From biased algorithms denying opportunities to surveillance systems tracking our every move, we’re building a future we might not want to live in.
The good news? It’s not too late to change course. But it requires admitting that move fast and break things maybe isn’t the best motto when the things you’re breaking are people’s lives.
Take Action Today
Want to be part of the solution instead of the problem? Here’s what you can do right now:
- Learn about AI ethics – Understanding the issues is the first step to addressing them
- Support ethical AI companies – Vote with your wallet for businesses doing it right
- Protect your data – Use privacy tools and limit what you share online
- Stay informed – Follow developments in AI regulation and policy
- Speak up – Contact representatives about AI concerns in your community
The future of AI isn’t predetermined. We still have time to shape it into something that serves humanity instead of exploiting it. But that window won’t stay open forever.
References:
-
Amazon’s Biased AI Hiring Tool: Amazon’s AI recruiting system showed bias against women, leading to its discontinuation. https://www.aclu.org/news/women-rights/why-amazons-automated-hiring-tool-discriminated-against-women
-
Racial Bias in Facial Recognition: Studies reveal higher error rates for darker-skinned individuals in facial recognition technology. https://www.aclu-mn.org/en/news/biased-technology-automated-discrimination-facial-recognition
-
Apple Card Gender Bias Allegations: The Apple Card faced criticism for allegedly offering lower credit limits to women with similar financial profiles. https://www.library.hbs.edu/baker-library/by-topic/gender-bias-complaints-against-apple-card-signal-dark-side-fintech
-
IBM Watson for Oncology’s Flaws: IBM Watson for Oncology was criticized for providing unsafe or incorrect advice due to training on synthetic data. https://www.ashclinicalnews.com/online-exclusives/incident-report/watson-supercomputer-recommended-unsafe-treatments/
-
Ethical Concerns of Deepfakes: Deepfake technology raises significant ethical issues regarding misinformation and deception. https://consensus.app/papers/ethics-implications-deepfake-technology-media-consensus/
-
EU AI Act: The European Union’s comprehensive AI Act categorizes AI systems by risk and sets compliance requirements. https://digital-strategy.ec.europa.eu/en/policies/ai-act
-
GDPR and AI Data Privacy: The GDPR imposes strict guidelines on data privacy and protection for AI development and deployment. https://securiti.ai/blog/gdpr-impact-on-ai/
-
US AI Bill of Rights: The White House proposed a framework to protect civil rights and promote democratic values in AI systems. https://www.ibm.com/blogs/research/2024/02/what-is-the-ai-bill-of-rights/
-
UN Guidelines on AI and Human Rights: The UN passed a resolution urging member states to safeguard human rights in AI development. https://www.un.org/sites/un2.un.org/files/2022/09/HLCP_Principles_Ethical_Use_AI_UN_System.pdf
-
China’s Social Credit System: China’s social credit system raises significant human rights concerns regarding privacy and freedom. https://ohrh.law.ox.ac.uk/the-human-rights-implications-of-chinas-social-credit-system/
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming our world, influencing everything from how we communicate to how we diagnose diseases. While AI offers tremendous potential for innovation, it also raises important ethical questions.
This article examines the ethical issues related to AI and the challenges of incorporating AI technologies into society.
Key Takeaways:
- Bias and Fairness: Actively work to identify and mitigate biases in AI systems.
- Transparency and Accountability: Develop explainable AI models and take responsibility for their outcomes.
- Ethical Guidelines: Follow established principles and support government regulations that promote responsible AI.
- Human-centric Approach: Ensure AI technologies enhance human well-being and respect human rights.
Understanding Artificial Intelligence

AI technologies include machine learning, natural language processing, robotics, and more recently, generative AI systems capable of creating content like text, images, or music.
AI Capabilities and Applications
- AI algorithms: used for data analysis and decision-making in various industries.
- AI Models: implemented in applications such as virtual assistants, recommendation systems, and autonomous vehicles.
- AI Tools: Software and platforms that enable AI functionalities, like image recognition or language translation.
The Ethical Implications of AI
Every day, AI systems make millions of decisions. They decide who gets a loan. Who sees a job posting. Who gets flagged at airport security. These aren’t future problems—they’re happening now.
The thing is, most people don’t even know when AI is making decisions about their lives. That mortgage application you submitted? An algorithm probably rejected it before a human ever saw it. That perfect job you never heard back from? AI might have tossed your resume in the digital trash.
The Bias Problem Nobody Wants to Fix
Here’s what happens when you train AI on human data: it learns human prejudices. Amazon discovered this the hard way when their AI-powered hiring tool started discriminating against women. The system learned from 10 years of resumes—mostly from men—and decided that being male was a qualification.
Common AI Biases:
- Racial bias in facial recognition (error rates up to 35% higher for darker-skinned individuals)
- Gender bias in language processing
- Economic bias in credit scoring algorithms
- Geographic bias in delivery and service algorithms
The companies building these systems know about these problems. They just don’t always care enough to fix them before launching.
Who’s Responsible When AI Screws Up?
Picture this: A self-driving car hits someone. Who goes to jail? The programmer who wrote the code? The company that made the car? The person sitting in the driver’s seat playing Candy Crush?
This isn’t some philosophical thought experiment. It’s a real question courts are trying to answer right now. And nobody has good answers yet.
The Accountability Gap
When humans make mistakes, we know who to blame. When AI makes mistakes, everyone points fingers:
| Who Gets Blamed | What They Say |
|---|---|
| Developers | “We just built what we were told” |
| Companies | “The algorithm made the decision” |
| Users | “We trusted the technology” |
| Regulators | “We’re still figuring out the rules” |
Meanwhile, real people suffer real consequences from AI decisions they can’t appeal or even understand.
Principles of Ethical AI
To address these challenges, several ethical principles guide AI development, including:
-
- Fairness: AI should not discriminate and should promote equitable treatment.
- Transparency: AI systems should be explainable and their decision-making processes understandable.
- Accountability: Developers and organizations must take responsibility for AI outcomes.
- Privacy: AI must protect user data and comply with data protection laws.
- Human-centric design: AI should enhance human capabilities and respect human rights.
The Privacy Trade-Off Everyone Ignores
AI needs data like cars need gas. The more data it has, the better it works. But that data comes from somewhere—it comes from us.
Every time you:
- Post on social media
- Use a fitness tracker
- Shop online
- Drive with GPS on
- Talk to a smart speaker
You’re feeding the machine. And once that data is out there, good luck getting it back.
What AI Knows About You
Modern AI systems can predict:
- When you’re likely to get sick
- If your relationship is failing
- Your political beliefs
- Your sexual orientation
- Whether you’re pregnant (sometimes before you know)
Companies say they anonymize this data. But researchers keep proving that anonymous data isn’t really anonymous. With enough data points, AI can figure out exactly who you are.
The Job Apocalypse That’s Already Started
Everyone talks about robots taking jobs in the future. But AI is already replacing workers today—just quietly.
Jobs AI Is Already Doing:
- Writing basic news articles
- Reviewing legal documents
- Diagnosing diseases
- Trading stocks
- Screening job applications
- Creating marketing content
- Answering customer service calls
The people who lost these jobs didn’t see it coming. One day they had work, the next day an algorithm did it cheaper and faster.
The Skills Gap Nobody’s Bridging
Here’s the cruel irony: The same companies replacing workers with AI say they can’t find qualified people to build and manage these systems. They’re creating a world where you either work on AI or get replaced by it.
Meanwhile, retraining programs are a joke. You can’t turn a 50-year-old truck driver into a machine learning engineer with a six-week coding bootcamp.
Real-Life Applications and Ethical Challenges
Practical Applications
This HTML Tool about AI Content Grader converts theoretical ethics discussion into actionable tool:
AI Content Grader
Analyze your content's originality, SEO potential, and readability
Originality
SEO Potential
Readability
Recommendations
Healthcare
AI technologies are revolutionizing healthcare delivery, from diagnosis to treatment planning. However, this integration raises critical ethical considerations about patient privacy and equitable access.
Ethical Challenges:
-
-
- Data Privacy: Handling patients’ sensitive health information requires strict compliance with privacy laws like HIPAA.
- Bias in Diagnosis: AI models trained on limited datasets may not perform well across diverse populations.
-
Real-Life Example:
-
-
- IBM Watson for Oncology was marketed as a tool for cancer treatment recommendations but received criticism for giving unsafe or incorrect advice, as it was trained on synthetic data instead of real patient cases.
-
Financial Services
The financial sector has embraced AI for various applications, including automated decision-making systems that handle everything from credit scoring to fraud detection.
Ethical Challenges:
-
-
- Algorithmic Bias: AI systems might inadvertently discriminate against certain groups in lending decisions.
- Lack of transparency: Customers may not understand how their data affects financial assessments.
-
Real-Life Example:
-
-
- Apple Card Controversy: In 2019, Apple’s credit card was criticized after allegations that its AI algorithm offered lower credit limits to women compared to men with similar financial profiles.
-
Generative AI Tools
Generative AI, like OpenAI’s GPT-3, can create content but raises unique ethical issues.
Ethical Challenges:
-
-
- Misinformation: Potential to generate realistic but false information.
- Intellectual Property: AI-generated content may infringe on existing works.
-
Real-Life Example:
-
-
- Deepfakes: AI-generated videos that realistically swap faces, which can be used maliciously to spread disinformation or harass individuals.
-
Addressing Bias and Ensuring Fairness
Implementing effective strategies to combat AI bias requires a multi-faceted approach.
Strategies:
-
-
- Diverse Datasets: Use representative data that includes various demographics.
- Bias Testing: Regularly test AI models for biased outcomes.
- Inclusive Teams: Promoting diversity and inclusivity in AI development teams helps bring different perspectives.
-
Table: Techniques for Reducing Bias in AI
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Augmentation | Enriching datasets with diverse examples |
| Algorithmic Fairness Metrics | Using metrics to measure and correct biases |
| Human Oversight | Incorporating human judgment in AI decision-making |
| Transparency Tools | Tools that explain AI decisions to users |
Government Regulations and Ethical Guidelines
Government policies and international frameworks play a vital role in setting ethical standards for AI.
AI Policies and International Frameworks
-
-
- AI Bill of Rights: Proposals to protect individuals from harms related to AI.
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): EU law that governs data protection and privacy.
- United Nations Guidelines on AI: Emphasize fairness, transparency, and human rights.
-
Real-Life Example:
-
-
- EU’s AI Act: A proposed regulatory framework that categorizes AI applications based on risk and sets compliance requirements to ensure safety and respect for fundamental rights.
-
The Future of AI and Ethics
Artificial General Intelligence
As we look ahead, the evolution of AI technology presents both opportunities and challenges. Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) raises new ethical questions about control and consciousness.
Ethical Considerations:
-
-
- Existential Risks: AGI could potentially surpass human control.
- Moral Status: Debates about whether AGI entities should have rights.
-
AI Adoption and Human Rights
Ensuring that AI adoption respects and promotes human rights is critical.
Ethical Concerns:
-
-
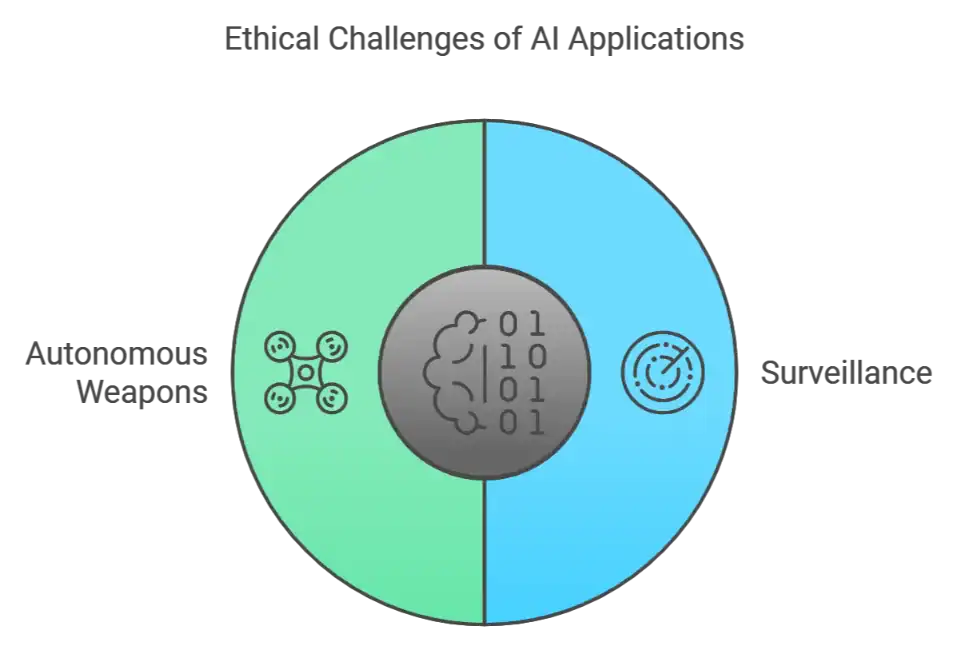
- Surveillance: AI technologies can be used to infringe on privacy.
- Autonomous Weapons: Ethical debates surround AI use in military applications.
-
Real-Life Example:
-
-
- Social Credit Systems: In some countries, AI is used to monitor and rate citizens’ behavior, raising significant privacy and freedom concerns.
-
What Can Actually Be Done?
Talking about problems is easy. Solving them is hard. But here’s what needs to happen:
1. Real Regulation (Not Just Talk)
Governments need to:
- Set clear rules for AI use
- Create penalties that actually hurt
- Require transparency in AI decisions
- Give people the right to appeal AI decisions
- Protect workers from AI replacement
The EU is trying with their AI Act. The US is still figuring out what AI even is.
2. Corporate Responsibility (Stop Laughing)
Companies using AI should:
- Test for bias before launching
- Explain how their AI makes decisions
- Let humans override AI choices
- Pay for retraining displaced workers
- Put ethics before profits
Yeah, I know. But we can dream.
3. Individual Awareness
You need to:
- Know when AI is making decisions about you
- Understand your rights (what few exist)
- Limit the data you share
- Support companies doing AI ethically
- Vote for politicians who get it
Because waiting for corporations to grow a conscience isn’t a strategy.
The Choice We Face
We’re at a crossroads. AI can either be a tool that helps humanity or a weapon that divides us further. The technology itself doesn’t care—it’s just math and electricity.
But the people building it, funding it, and deploying it? They make choices every day. And right now, they’re mostly choosing profits over people.
The ethical implications of AI aren’t some far-off concern. They’re here, now, affecting real people in real ways. From biased algorithms denying opportunities to surveillance systems tracking our every move, we’re building a future we might not want to live in.
The good news? It’s not too late to change course. But it requires admitting that move fast and break things maybe isn’t the best motto when the things you’re breaking are people’s lives.
Take Action Today
Want to be part of the solution instead of the problem? Here’s what you can do right now:
- Learn about AI ethics – Understanding the issues is the first step to addressing them
- Support ethical AI companies – Vote with your wallet for businesses doing it right
- Protect your data – Use privacy tools and limit what you share online
- Stay informed – Follow developments in AI regulation and policy
- Speak up – Contact representatives about AI concerns in your community
The future of AI isn’t predetermined. We still have time to shape it into something that serves humanity instead of exploiting it. But that window won’t stay open forever.
References:
-
Amazon’s Biased AI Hiring Tool: Amazon’s AI recruiting system showed bias against women, leading to its discontinuation. https://www.aclu.org/news/women-rights/why-amazons-automated-hiring-tool-discriminated-against-women
-
Racial Bias in Facial Recognition: Studies reveal higher error rates for darker-skinned individuals in facial recognition technology. https://www.aclu-mn.org/en/news/biased-technology-automated-discrimination-facial-recognition
-
Apple Card Gender Bias Allegations: The Apple Card faced criticism for allegedly offering lower credit limits to women with similar financial profiles. https://www.library.hbs.edu/baker-library/by-topic/gender-bias-complaints-against-apple-card-signal-dark-side-fintech
-
IBM Watson for Oncology’s Flaws: IBM Watson for Oncology was criticized for providing unsafe or incorrect advice due to training on synthetic data. https://www.ashclinicalnews.com/online-exclusives/incident-report/watson-supercomputer-recommended-unsafe-treatments/
-
Ethical Concerns of Deepfakes: Deepfake technology raises significant ethical issues regarding misinformation and deception. https://consensus.app/papers/ethics-implications-deepfake-technology-media-consensus/
-
EU AI Act: The European Union’s comprehensive AI Act categorizes AI systems by risk and sets compliance requirements. https://digital-strategy.ec.europa.eu/en/policies/ai-act
-
GDPR and AI Data Privacy: The GDPR imposes strict guidelines on data privacy and protection for AI development and deployment. https://securiti.ai/blog/gdpr-impact-on-ai/
-
US AI Bill of Rights: The White House proposed a framework to protect civil rights and promote democratic values in AI systems. https://www.ibm.com/blogs/research/2024/02/what-is-the-ai-bill-of-rights/
-
UN Guidelines on AI and Human Rights: The UN passed a resolution urging member states to safeguard human rights in AI development. https://www.un.org/sites/un2.un.org/files/2022/09/HLCP_Principles_Ethical_Use_AI_UN_System.pdf
-
China’s Social Credit System: China’s social credit system raises significant human rights concerns regarding privacy and freedom. https://ohrh.law.ox.ac.uk/the-human-rights-implications-of-chinas-social-credit-system/
I’m Alexios Papaioannou, an experienced affiliate marketer and content creator. With a decade of expertise, I excel in crafting engaging blog posts to boost your brand. My love for running fuels my creativity. Let’s create exceptional content together!